Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA
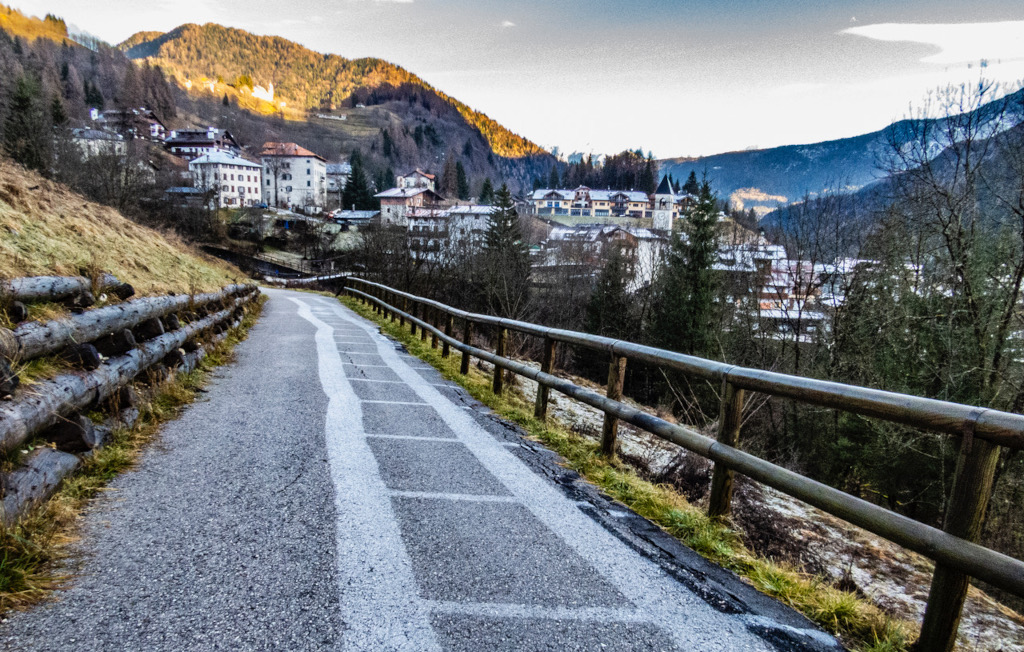
A Solstice Sun Tattoo
20/12/2025
The word solstice is from the Latin for Sun and to pause or stand still. And in the days surrounding a solstice the Sun's annual north-south drift in planet Earth's sky does slow down, pause, and then reverse direction. So near the solstice the daily path of the Sun through the sky really doesn't change much. In fact, near the December solstice, the Sun's consistent, low arc through northern hemisphere skies, along with low surface temperatures, has left a noticeable imprint on this path to the mountain town of Peaio in northern Italy. The morning frost on the road has melted away only where the sunlight was able to reach the ground. But it remains in the areas persistently shadowed by the fence, tattooing in frost an image of the fence on the asphalt surface.
Copyright: Marcella Pace
Προηγούμενες Αστρονομικές Εικόνες της Ημέρας από τη NASA
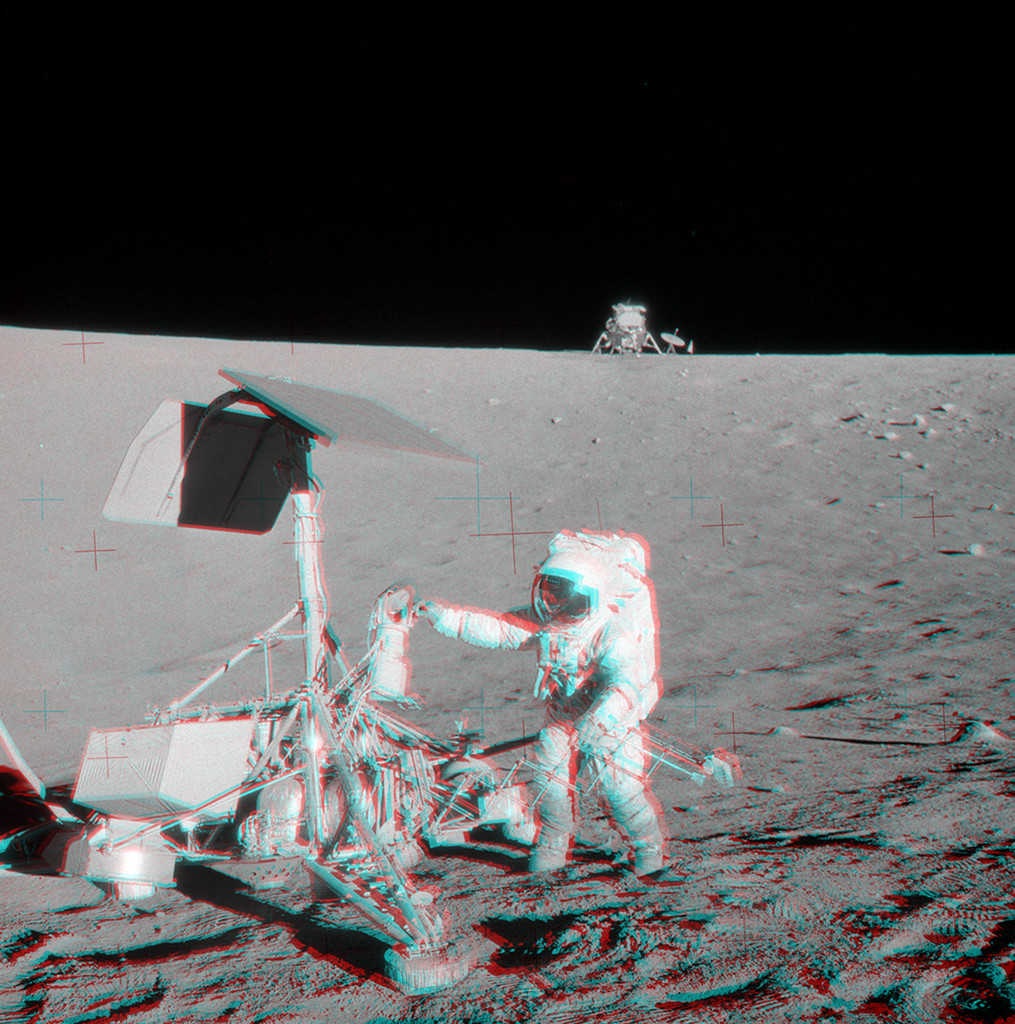
Apollo 12 and Surveyor 3
15/11/2024
Put on your red/blue glasses and gaze across the western Ocean of Storms on the surface of the Moon. The 3D anaglyph features Apollo 12 astronaut Pete Conrad visiting the Surveyor 3 spacecraft in November of 1969. Surveyor 3 had landed at the site on the inside slope of a small crater about 2 1/2 years earlier in April of 1967. Visible on the horizon beyond the far crater wall, Apollo 12's Lunar Module Intrepid touched down less than 200 meters (650 feet) away, easy moonwalking distance from the robotic Surveyor spacecraft. This stereo image was carefully created from two separate pictures (AS12-48-7133, AS12-48-7134) captured on the lunar surface. They depict the scene from only slightly different viewpoints, approximating the separation between human eyes.
Copyright: NASA
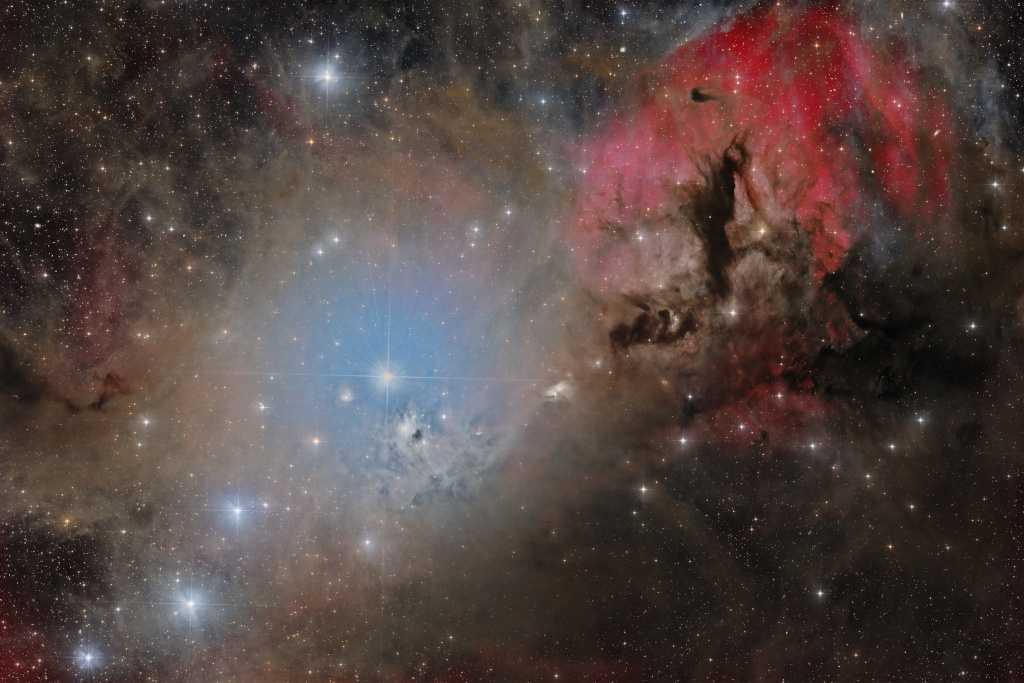
IC 348 and Barnard 3
14/11/2024
A great nebulous region near bright star omicron Persei offers this study in cosmic contrasts. Captured in the telescopic frame the colorful complex of dust, gas, and stars spans about 3 degrees on the sky along the edge of the Perseus molecular cloud some 1000 light-years away. Surrounded by a bluish halo of dust reflected starlight, omicron Persei itself is just left of center. Immediately below it lies the intriguing young star cluster IC 348 recently explored by the James Webb Space Telescope. In silhouette against the diffuse reddish glow of hydrogen gas, dark and obscuring interstellar dust cloud Barnard 3 is at upper right. Of course the cosmic dust also tends to hide newly formed stars and young stellar objects or protostars from prying optical telescopes. At the Perseus molecular cloud's estimated distance, this field of view would span about 50 light-years.
Copyright: Ashraf Abu Sara
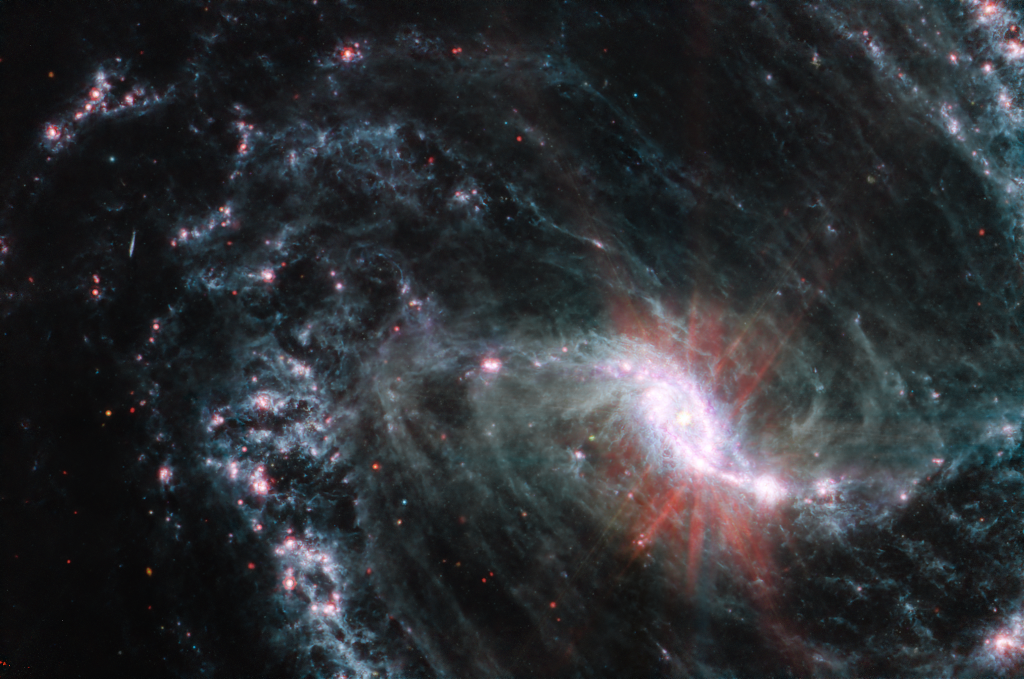
Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 1365 from Webb
13/11/2024
A mere 56 million light-years distant toward the southern constellation Fornax, NGC 1365 is an enormous barred spiral galaxy about 200,000 light-years in diameter. That's twice the size of our own barred spiral Milky Way. This sharp image from the James Webb Space Telescope's Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) reveals stunning details of this magnificent spiral in infrared light. Webb's field of view stretches about 60,000 light-years across NGC 1365, exploring the galaxy's core and bright newborn star clusters. The intricate network of dusty filaments and bubbles is created by young stars along spiral arms winding from the galaxy's central bar. Astronomers suspect the gravity field of NGC 1365's bar plays a crucial role in the galaxy's evolution, funneling gas and dust into a star-forming maelstrom and ultimately feeding material into the active galaxy's central, supermassive black hole.
Copyright: NASA
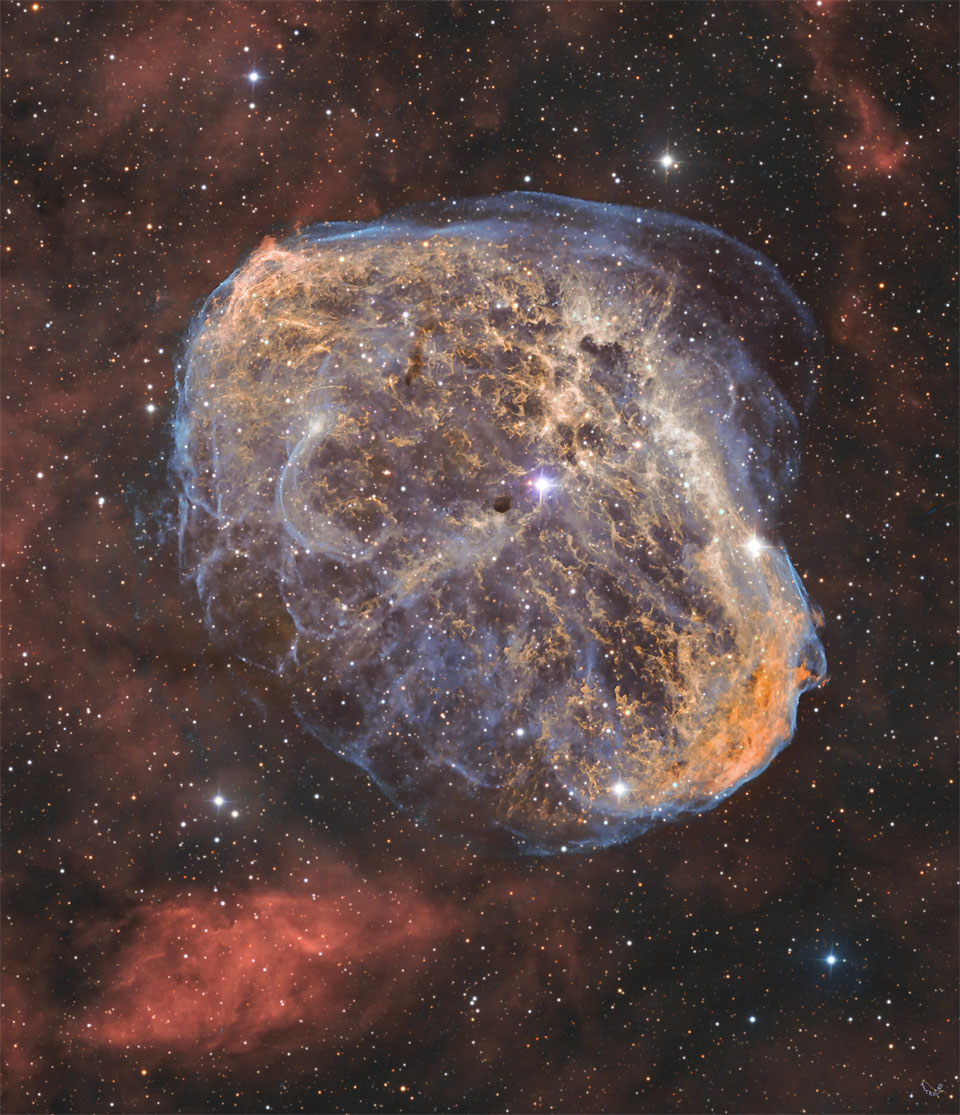
NGC 6888: The Crescent Nebula
12/11/2024
How was the Crescent Nebula created? Looking like an emerging space cocoon, the Crescent Nebula, visible in the center of the featured image, was created by the brightest star in its center. A leading progenitor hypothesis has the Crescent Nebula beginning to form about 250,000 years ago. At that time, the massive central star had evolved to become a Wolf-Rayet star (WR 136), shedding its outer envelope in a strong stellar wind, ejecting the equivalent of our Sun's mass every 10,000 years. This wind impacted surrounding gas left over from a previous phase, compacting it into a series of complex shells, and lighting it up. The Crescent Nebula, also known as NGC 6888, lies about 4,700 light-years away in the constellation of Cygnus. Star WR 136 will probably undergo a supernova explosion sometime in the next million years. Jigsaw Challenge: Astronomy Puzzle of the Day
Copyright: Team ARO
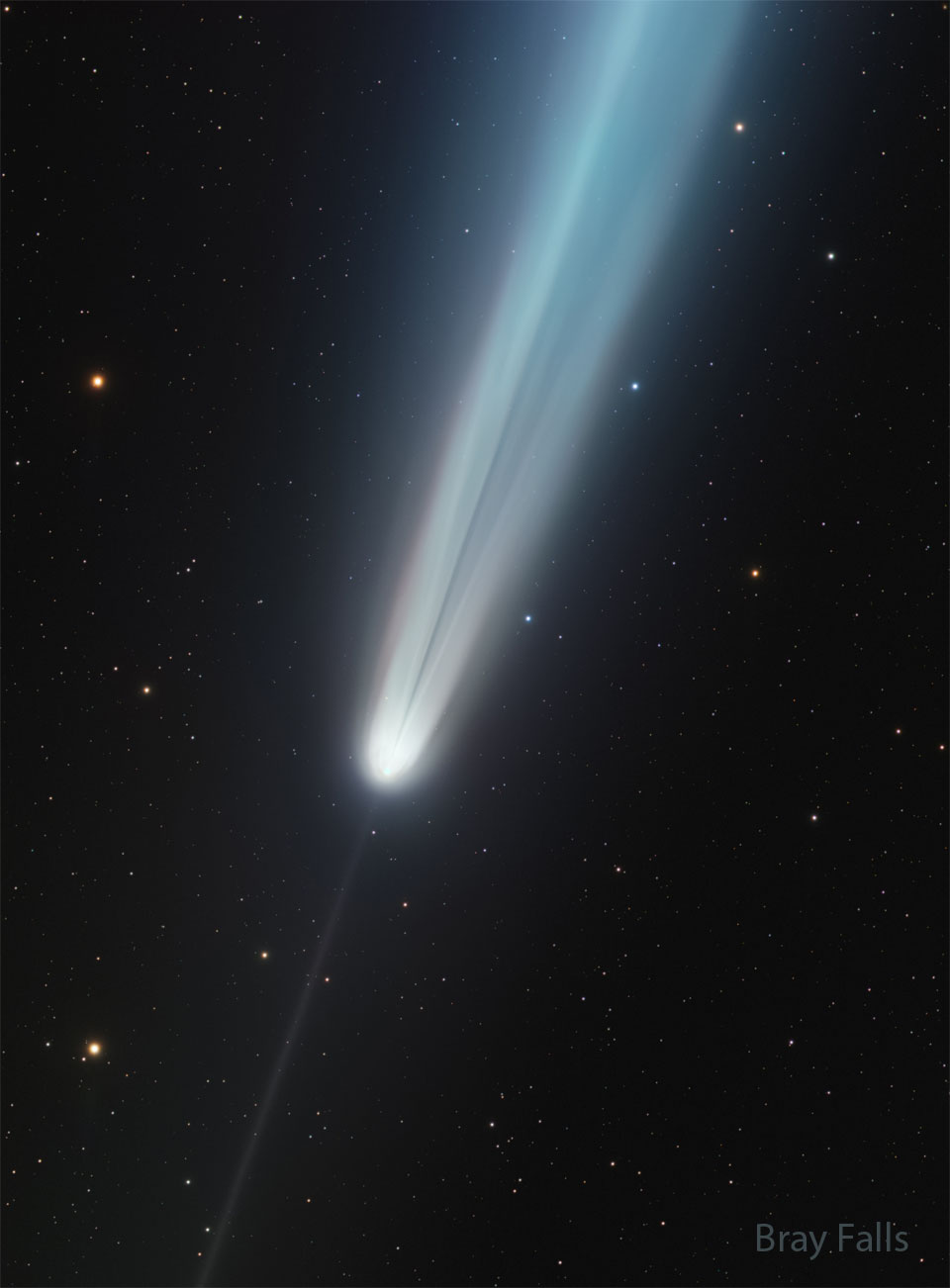
The Unusual Tails of Comet Tsuchinshan-Atlas
11/11/2024
What created an unusual dark streak in Comet Tsuchinshan-Atlas's tail? Some images of the bright comet during mid-October not only caught its impressively long tail and its thin anti-tail, but a rather unexpected feature: a dark streak in the long tail. The reason for the dark streak is currently unclear and a topic of some debate. Possible reasons include a plume of dark dust, different parts of the bright tail being unusually superposed, and a shadow of a dense part of the coma on smaller dust particles. The streak is visible in the featured image taken on October 14 from Texas, USA. To help future analyses, if you have taken a good image of the comet that clearly shows this dark streak, please send it in to APOD. Comet Tsuchinshan–ATLAS has now faded considerably and is returning to the outer Solar System. Gallery: Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS in 2024
Copyright: Bray Falls
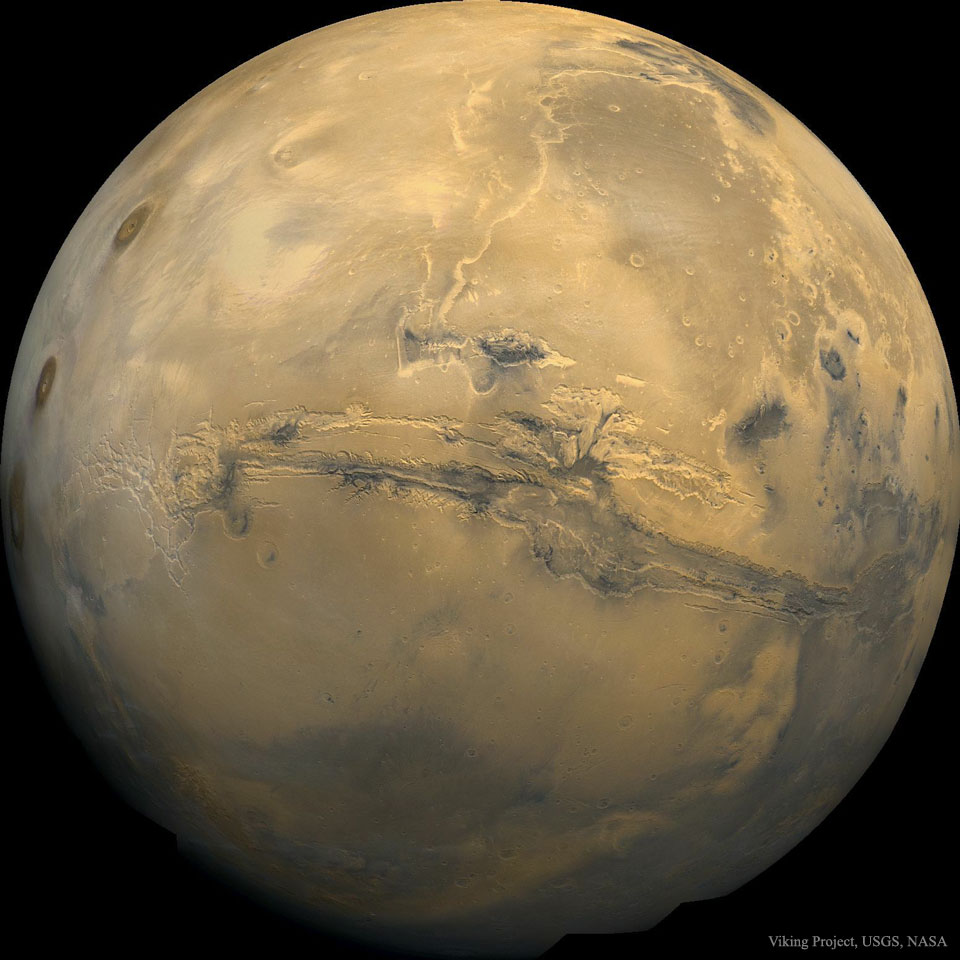
Valles Marineris: The Grand Canyon of Mars
10/11/2024
The largest canyon in the Solar System cuts a wide swath across the face of Mars. Named Valles Marineris, the grand valley extends over 3,000 kilometers long, spans as much as 600 kilometers across, and delves as much as 8 kilometers deep. By comparison, the Earth's Grand Canyon in Arizona, USA is 800 kilometers long, 30 kilometers across, and 1.8 kilometers deep. The origin of the Valles Marineris remains unknown, although a leading hypothesis holds that it started as a crack billions of years ago as the planet cooled. Several geologic processes have been identified in the canyon. The featured mosaic was created from over 100 images of Mars taken by Viking Orbiters in the 1970s.
Copyright: NASA
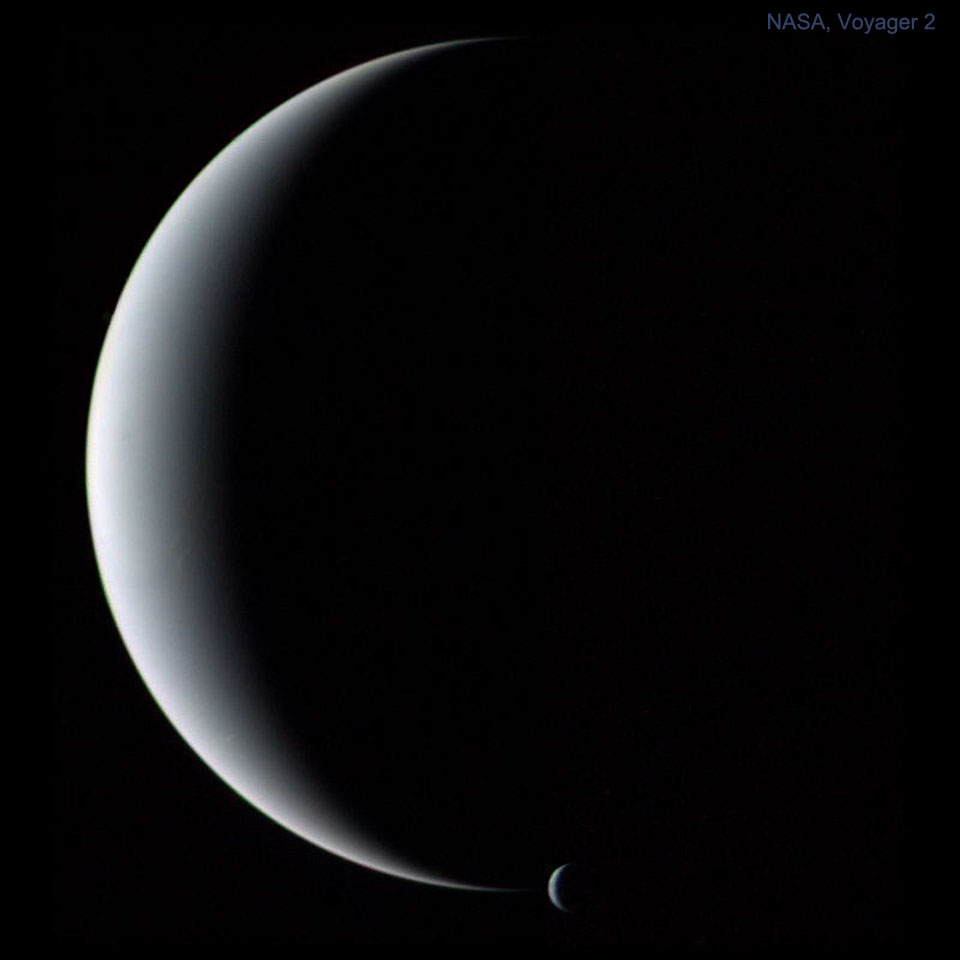
Neptune at Night
09/11/2024
Ice giant Neptune is faint in Earth's night sky. Some 30 times farther from the Sun than our fair planet, telescopes are needed to catch a glimpse of the dim and distant world. This dramatic view of Neptune's night just isn't possible for telescopes in the vicinity of planet Earth though. Peering out from the inner Solar System they can only bring Neptune's day side into view. In fact this night side image with Neptune's slender crescent next to the crescent of its large moon Triton was captured by Voyager 2. Launched from planet Earth in 1977 the Voyager 2 spacecraft made a close fly by of the Solar System's outermost planet in 1989, looking back on Neptune as the robotic spacecraft continued its voyage to interstellar space.
Copyright: Voyager
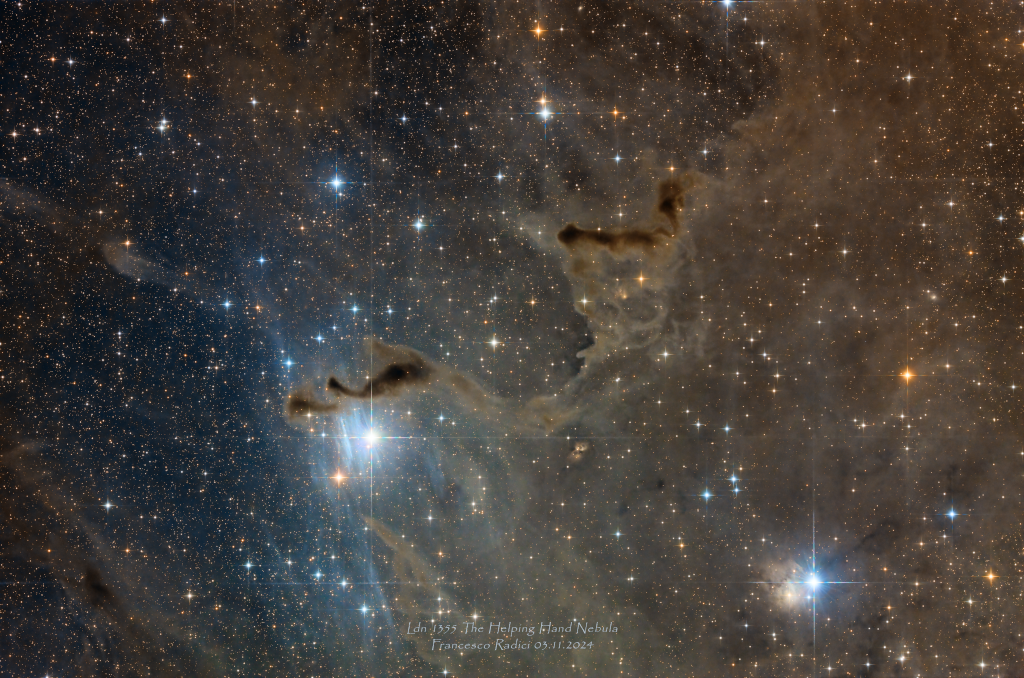
Helping Hand in Cassiopeia
08/11/2024
Drifting near the plane of our Milky Way galaxy these dusty molecular clouds seem to extend a helping hand on a cosmic scale. Part of a local complex of star-forming interstellar clouds they include LDN 1358, 1357, and 1355 from American astronomer Beverly Lynds' 1962 Catalog of Dark Nebulae. Presenting a challenging target for astro-imagers, the obscuring dark nebulae are nearly 3,000 light-years away, toward rich starfields in the northern constellation Cassiopeia. At that distance, this deep, telescopic field of view would span about 80 light-years.
Copyright: Francesco Radici
Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA (NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day) είναι μια δωρεάν υπηρεσία που παρέχει καθημερινά μια εντυπωσιακή εικόνα από το σύμπαν, την λήψη της οποίας έχει πραγματοποιήσει κάποιος από τους αστρονόμους της NASA ή από κάποιον από τους δορυφόρους ή τα τηλεσκόπια που η NASA λειτουργεί. Οι εικόνες που εμφανίζονται καλύπτουν μια ευρεία γκάμα από θέματα, συμπεριλαμβανομένων των αστερισμών, των γαλαξιών, των πλανητικών συστημάτων, των κομητών, των αστρικών σωμάτων και των παρατηρητηρίων. Κάθε εικόνα συνοδεύεται από μια σύντομη εξήγηση και πληροφορίες σχετικά με το τι παρατηρείται στην εικόνα.