Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA
A Solstice Sun Tattoo
20/12/2025
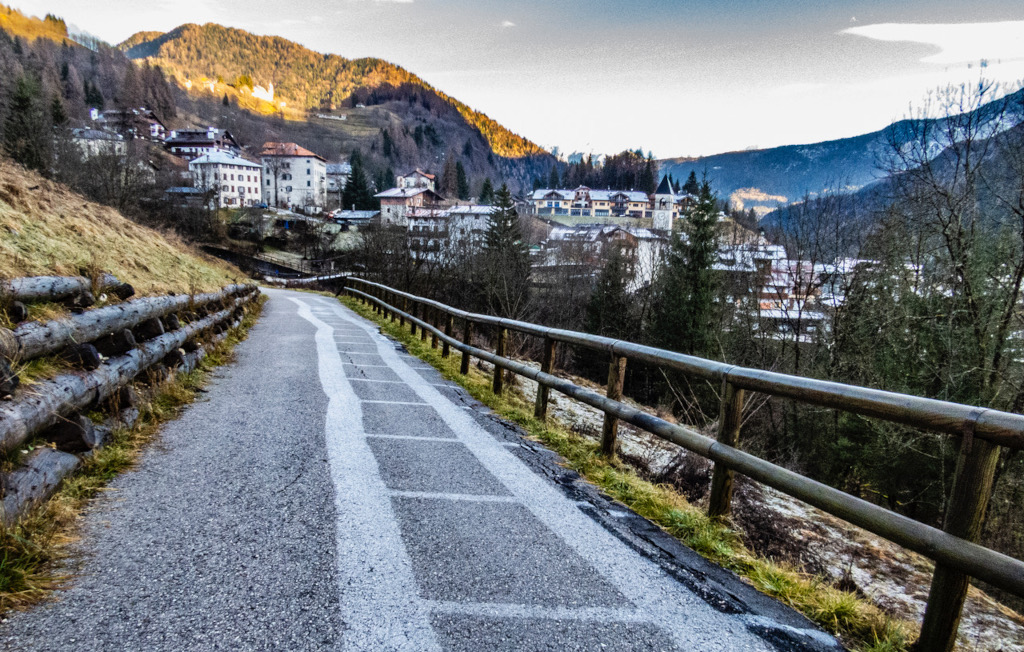
The word solstice is from the Latin for Sun and to pause or stand still. And in the days surrounding a solstice the Sun's annual north-south drift in planet Earth's sky does slow down, pause, and then reverse direction. So near the solstice the daily path of the Sun through the sky really doesn't change much. In fact, near the December solstice, the Sun's consistent, low arc through northern hemisphere skies, along with low surface temperatures, has left a noticeable imprint on this path to the mountain town of Peaio in northern Italy. The morning frost on the road has melted away only where the sunlight was able to reach the ground. But it remains in the areas persistently shadowed by the fence, tattooing in frost an image of the fence on the asphalt surface.
Copyright: Marcella Pace
Προηγούμενες Αστρονομικές Εικόνες της Ημέρας από τη NASA
Black Hole Accreting with Jet
07/05/2024
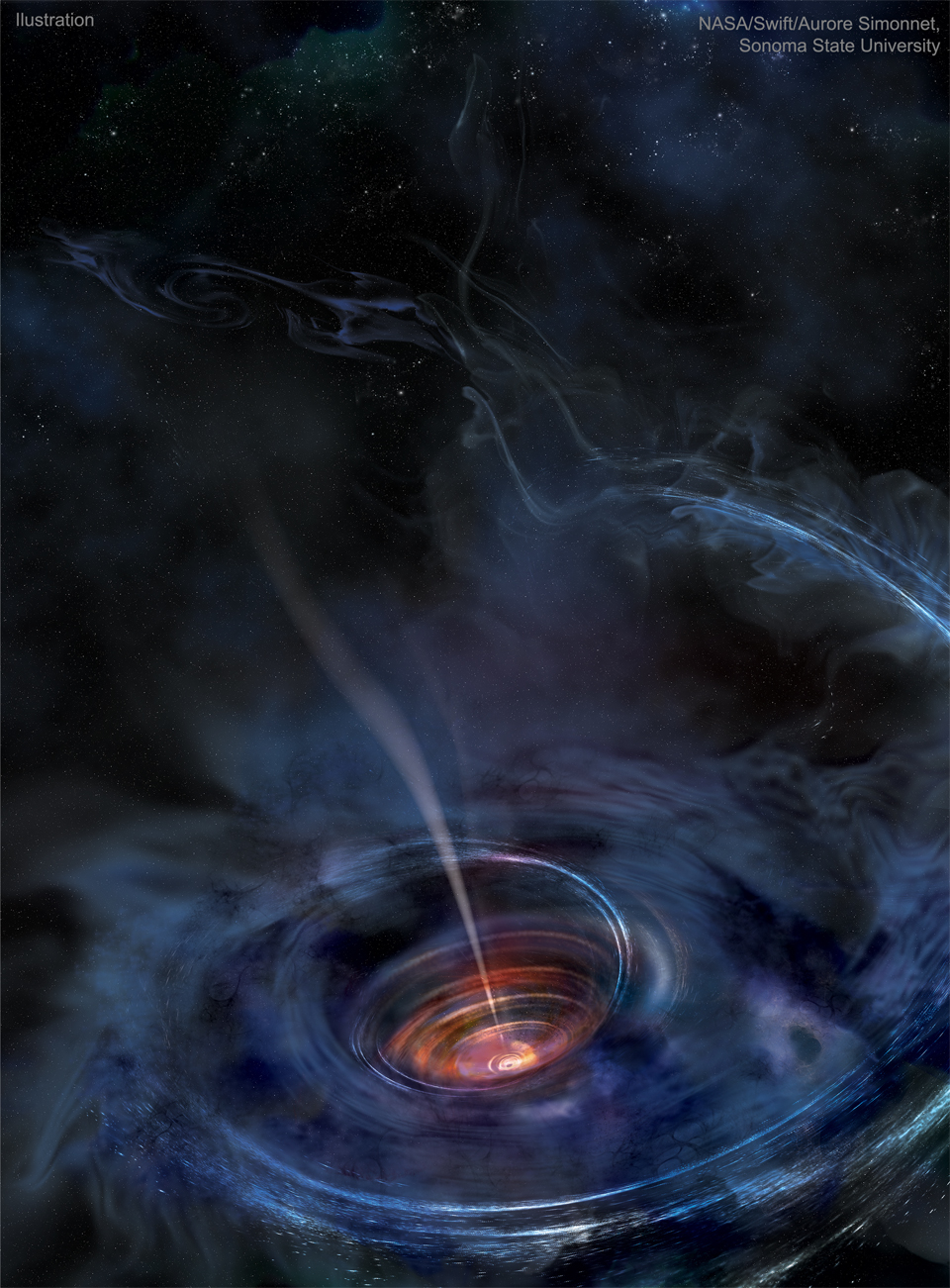
What happens when a black hole devours a star? Many details remain unknown, but observations are providing new clues. In 2014, a powerful explosion was recorded by the ground-based robotic telescopes of the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (Project ASAS-SN), with followed-up observations by instruments including NASA's Earth-orbiting Swift satellite. Computer modeling of these emissions fit a star being ripped apart by a distant supermassive black hole. The results of such a collision are portrayed in the featured artistic illustration. The black hole itself is a depicted as a tiny black dot in the center. As matter falls toward the hole, it collides with other matter and heats up. Surrounding the black hole is an accretion disk of hot matter that used to be the star, with a jet emanating from the black hole's spin axis. Fall towards eternity: It's Black Hole Week at NASA!
Copyright: NASA
A Total Solar Eclipse from Sliver to Ring
06/05/2024
This is how the Sun disappeared from the daytime sky last month. The featured time-lapse video was created from stills taken from Mountain View, Arkansas, USA on 2024 April 8. First, a small sliver of a normally spotted Sun went strangely dark. Within a few minutes, much of the background Sun was hidden behind the advancing foreground Moon. Within an hour, the only rays from the Sun passing the Moon appeared like a diamond ring. During totality, most of the surrounding sky went dark, making the bright pink prominences around the Sun's edge stand out, and making the amazing corona appear to spread into the surrounding sky. The central view of the corona shows an accumulation of frames taken during complete totality. As the video ends, just a few minutes later, another diamond ring appeared -- this time on the other side of the Moon. Within the next hour, the sky returned to normal. Celebrate the Voids: It's Black Hole Week at NASA!
Copyright: Reinhold Wittich; Music: Sunrise from Also sprach Zarathusra (R. Strauss) by Sascha Ende
A Black Hole Disrupts a Passing Star
05/05/2024
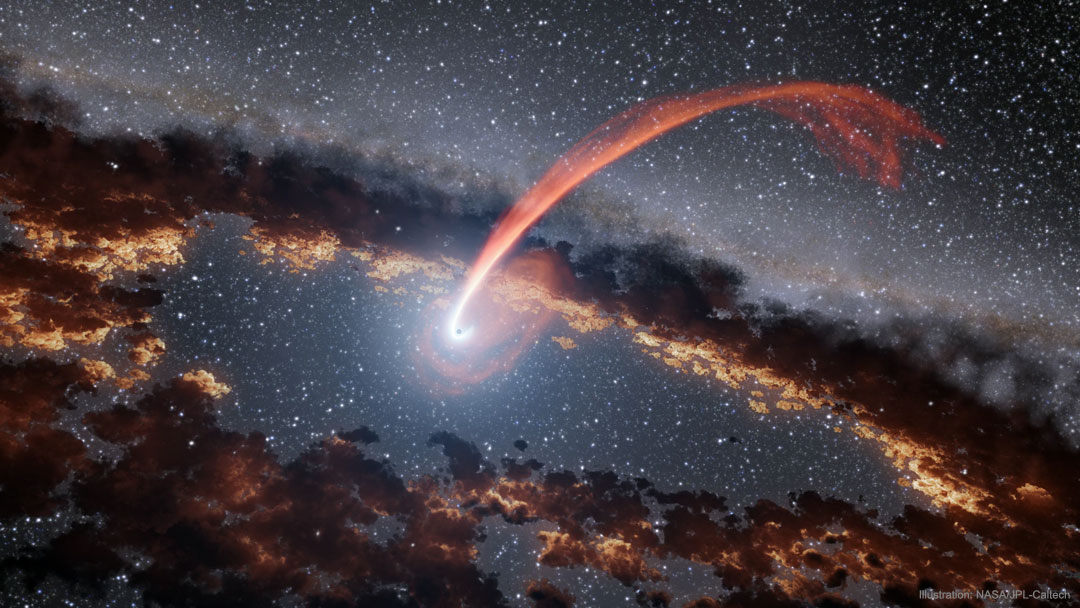
What happens to a star that goes near a black hole? If the star directly impacts a massive black hole, then the star falls in completely -- and everything vanishes. More likely, though, the star goes close enough to have the black hole's gravity pull away its outer layers, or disrupt, the star. Then, most of the star's gas does not fall into the black hole. These stellar tidal disruption events can be as bright as a supernova, and an increasing amount of them are being discovered by automated sky surveys. In the featured artist's illustration, a star has just passed a massive black hole and sheds gas that continues to orbit. The inner edge of a disk of gas and dust surrounding the black hole is heated by the disruption event and may glow long after the star is gone. Hole New Worlds: It's Black Hole Week at NASA!
Copyright: NASA
3 ATs
04/05/2024
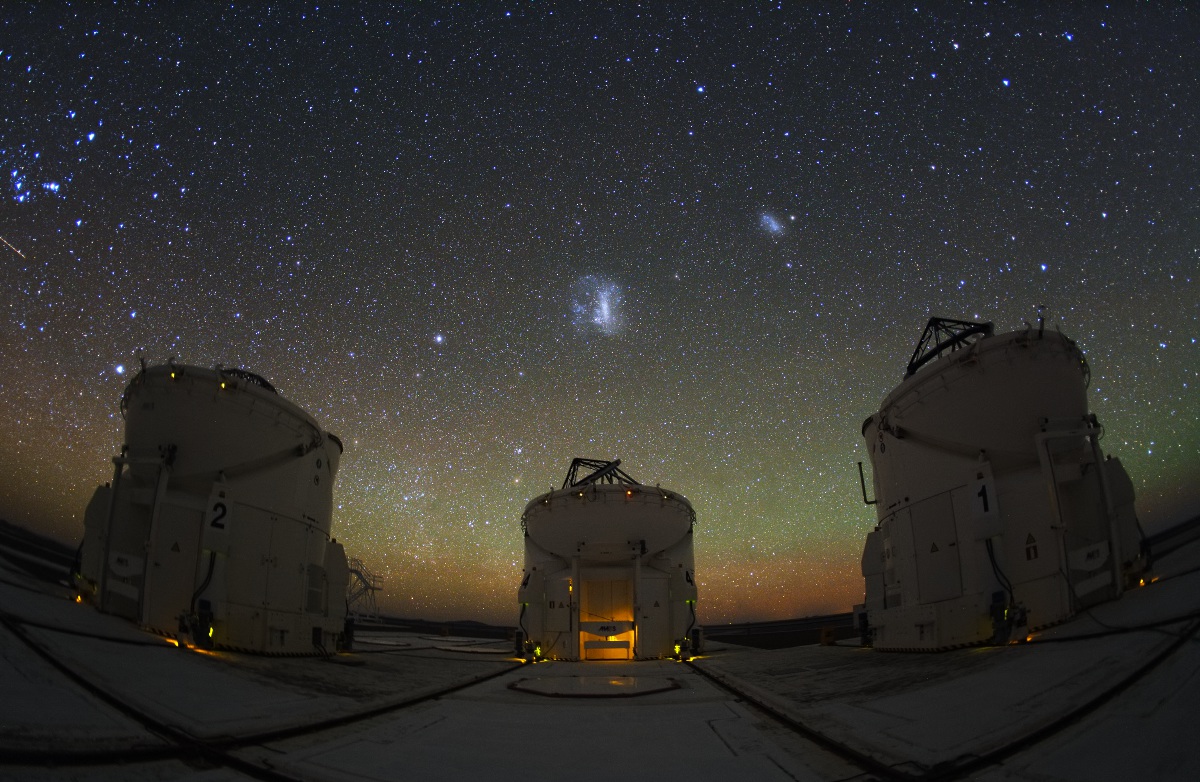
Despite their resemblance to R2D2, these three are not the droids you're looking for. Instead, the enclosures house 1.8 meter Auxiliary Telescopes (ATs) at Paranal Observatory in the Atacama Desert region of Chile. The ATs are designed to be used for interferometry, a technique for achieving extremely high resolution observations, in concert with the observatory's 8 meter Very Large Telescope units. A total of four ATs are operational, each fitted with a transporter that moves the telescope along a track allowing different arrays with the large unit telescopes. To work as an interferometer, the light from each telescope is brought to a common focal point by a system of mirrors in underground tunnels. Above these three ATs, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds are the far, far away satellite galaxies of our own Milky Way. In the clear and otherwise dark southern skies, planet Earth's greenish atmospheric airglow stretches faintly along the horizon.
Copyright: Yuri Beletsky
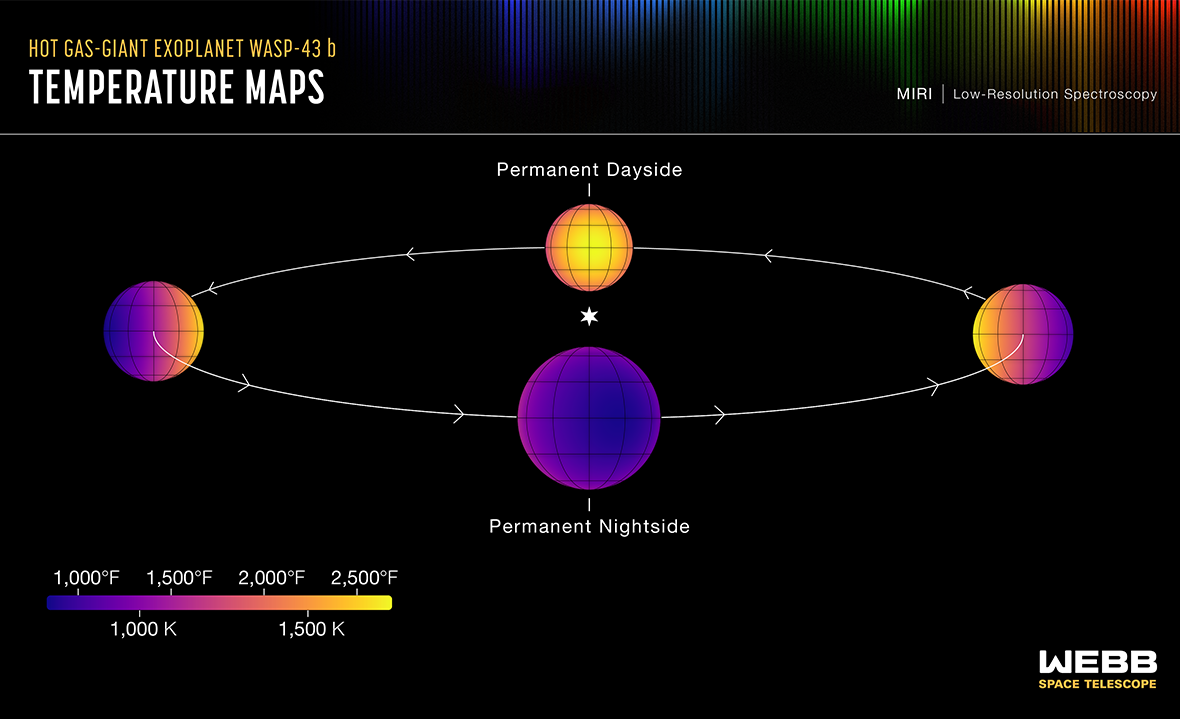
Temperatures on Exoplanet WASP-43b
03/05/2024
A mere 280 light-years from Earth, tidally locked, Jupiter-sized exoplanet WASP-43b orbits its parent star once every 0.8 Earth days. That puts it about 2 million kilometers (less than 1/25th the orbital distance of Mercury) from a small, cool sun. Still, on a dayside always facing its parent star, temperatures approach a torrid 2,500 degrees F as measured at infrared wavelengths by the MIRI instrument on board the James Webb Space Telescope. In this illustration of the hot exoplanet's orbit, Webb measurements also show nightside temperatures remain above 1,000 degrees F. That suggests that strong equatorial winds circulate the dayside atmospheric gases to the nightside before they can completely cool off. Exoplanet WASP-43b is now formally known as Astrolábos, and its K-type parent star has been christened Gnomon. Webb's infrared spectra indicate water vapor is present on the nightside as well as the dayside of the planet, providing information about cloud cover on Astrolábos.
Copyright: NASA
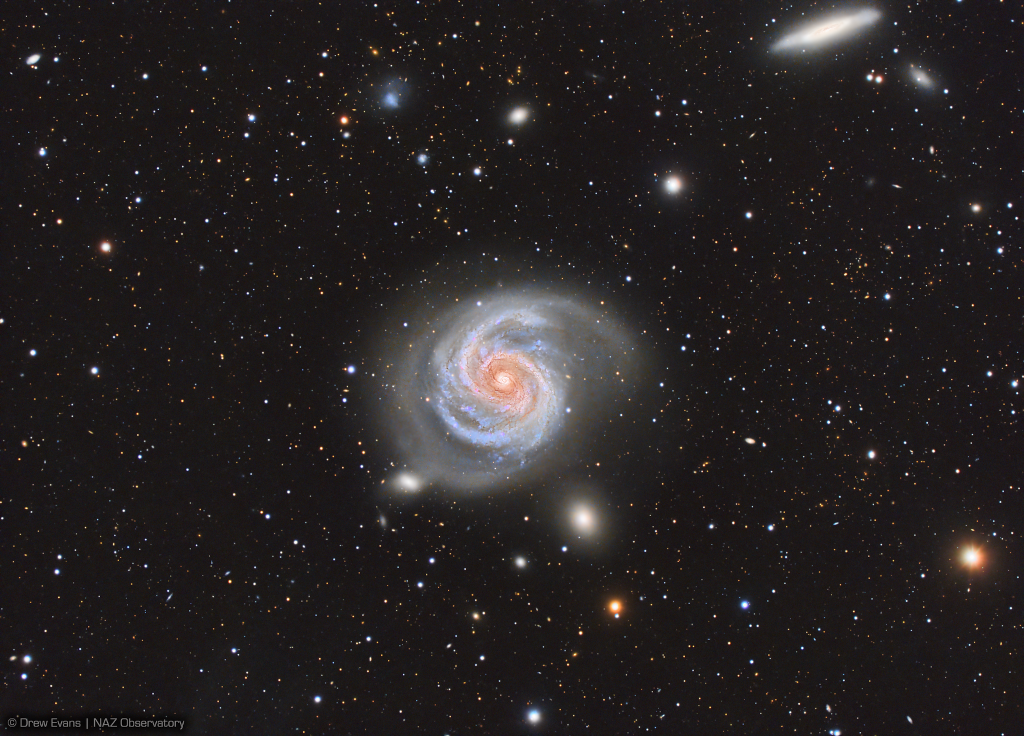
M100: A Grand Design Spiral Galaxy
02/05/2024
Majestic on a truly cosmic scale, M100 is appropriately known as a grand design spiral galaxy. The large galaxy of over 100 billion stars has well-defined spiral arms, similar to our own Milky Way. One of the brightest members of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies, M100, also known as NGC 4321 is 56 million light-years distant toward the well-groomed constellation Coma Berenices. In this telescopic image, the face-on grand design spiral shares a nearly 1 degree wide field-of-view with slightly less conspicuous edge-on spiral NGC 4312 (at upper right). The 21 hour long equivalent exposure from a dark sky site near Flagstaff, Arizona, planet Earth, reveals M100's bright blue star clusters and intricate winding dust lanes which are hallmarks of this class of galaxies. Measurements of variable stars in M100 have played an important role in determining the size and age of the Universe.
Copyright: Drew Evans
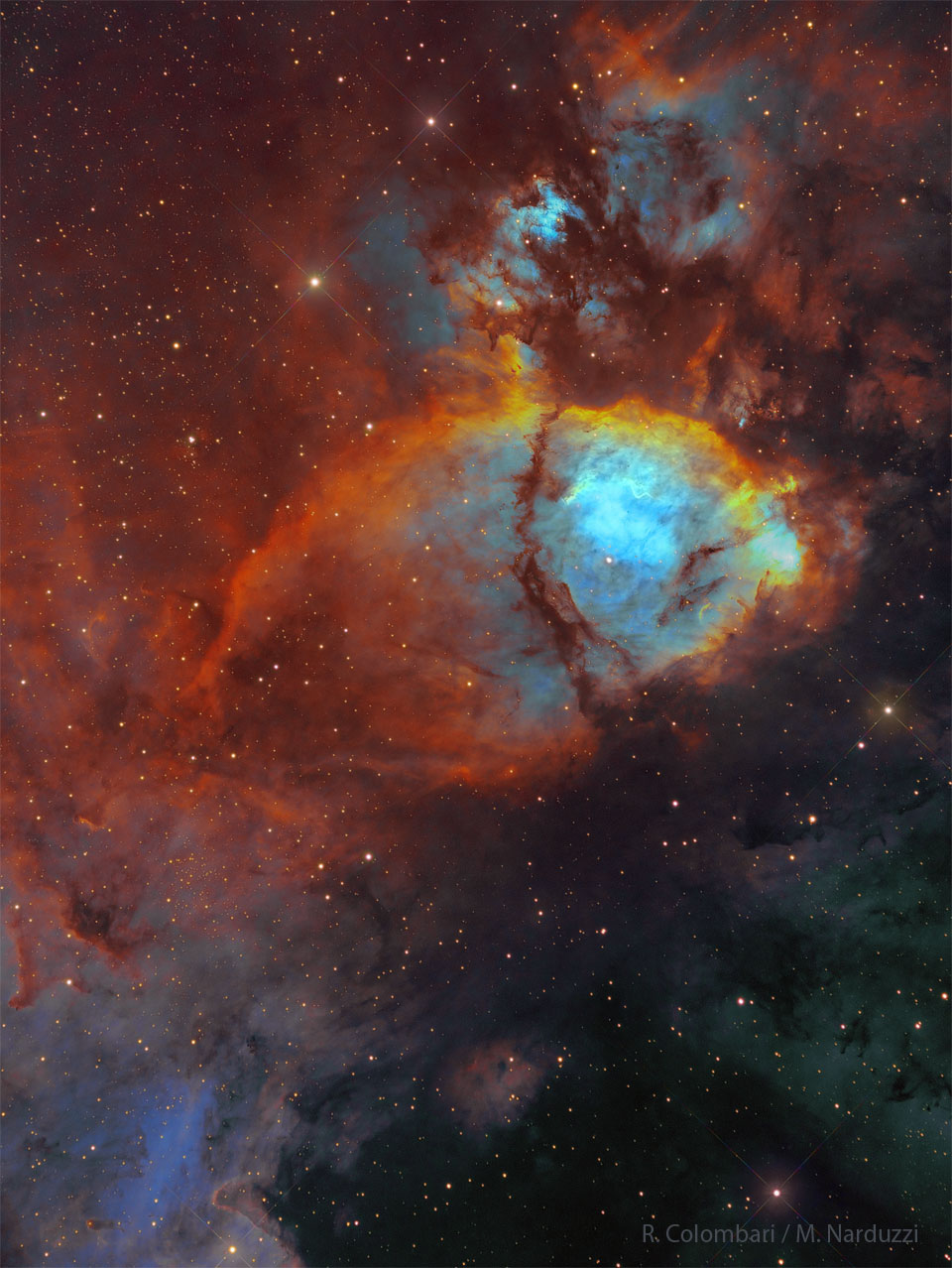
IC 1795: The Fishhead Nebula
01/05/2024
To some, this nebula looks like the head of a fish. However, this colorful cosmic portrait really features glowing gas and obscuring dust clouds in IC 1795, a star forming region in the northern constellation Cassiopeia. The nebula's colors were created by adopting the Hubble color palette for mapping narrowband emissions from oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur atoms to blue, green and red colors, and further blending the data with images of the region recorded through broadband filters. Not far on the sky from the famous Double Star Cluster in Perseus, IC 1795 is itself located next to IC 1805, the Heart Nebula, as part of a complex of star forming regions that lie at the edge of a large molecular cloud. Located just over 6,000 light-years away, the larger star forming complex sprawls along the Perseus spiral arm of our Milky Way Galaxy. At that distance, IC 1795 would span about 70 light-years across. Open Science: Browse 3,300+ codes in the Astrophysics Source Code Library
Copyright: Roberto Colombari & Mauro Narduzzi
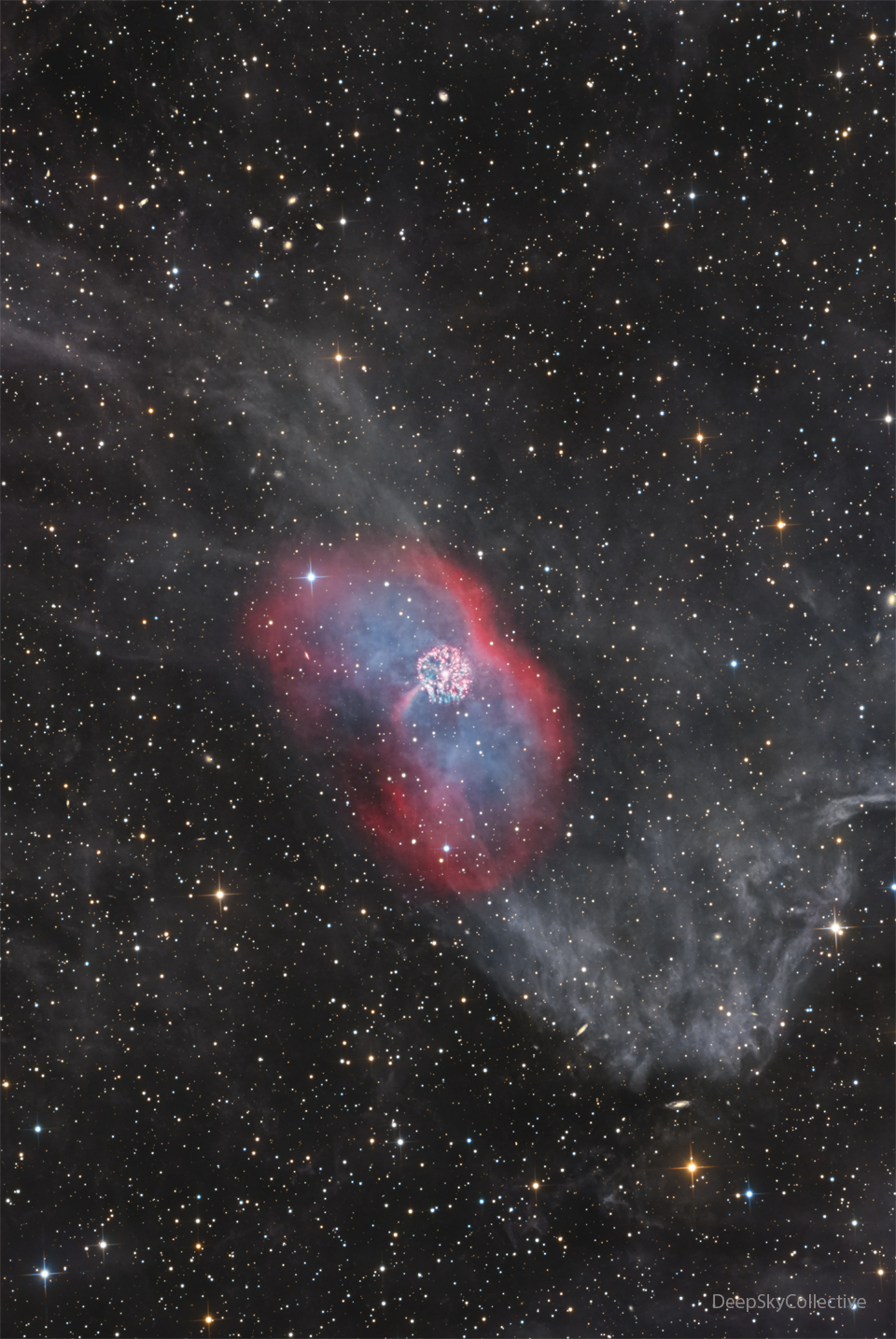
GK Per: Nova and Planetary Nebula
30/04/2024
The star system GK Per is known to be associated with only two of the three nebulas pictured. At 1500 light years distant, Nova Persei 1901 (GK Persei) was the second closest nova yet recorded. At the very center is a white dwarf star, the surviving core of a former Sun-like star. It is surrounded by the circular Firework nebula, gas that was ejected by a thermonuclear explosion on the white dwarf's surface -- a nova -- as recorded in 1901. The red glowing gas surrounding the Firework nebula is the atmosphere that used to surround the central star. This gas was expelled before the nova and appears as a diffuse planetary nebula. The faint gray gas running across is interstellar cirrus that seems to be just passing through coincidently. In 1901, GK Per's nova became brighter than Betelgeuse. Similarly, star system T CrB is expected to erupt in a nova later this year, but we don't know exactly when nor how bright it will become.
Copyright: Deep Sky Collective
Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA (NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day) είναι μια δωρεάν υπηρεσία που παρέχει καθημερινά μια εντυπωσιακή εικόνα από το σύμπαν, την λήψη της οποίας έχει πραγματοποιήσει κάποιος από τους αστρονόμους της NASA ή από κάποιον από τους δορυφόρους ή τα τηλεσκόπια που η NASA λειτουργεί. Οι εικόνες που εμφανίζονται καλύπτουν μια ευρεία γκάμα από θέματα, συμπεριλαμβανομένων των αστερισμών, των γαλαξιών, των πλανητικών συστημάτων, των κομητών, των αστρικών σωμάτων και των παρατηρητηρίων. Κάθε εικόνα συνοδεύεται από μια σύντομη εξήγηση και πληροφορίες σχετικά με το τι παρατηρείται στην εικόνα.