Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA
Gemini Meteors over Snow Capped Mountains
15/12/2025
Where are all of these meteors coming from? In terms of direction on the sky, the pointed answer is the constellation of Gemini. That is why the major meteor shower in December is known as the Geminids -- because shower meteors all appear to come from a radiant toward Gemini. Three dimensionally, however, sand-sized debris expelled from the unusual asteroid 3200 Phaethon follows a well-defined orbit about our Sun, and the part of the orbit that approaches Earth is superposed in front of the constellation of Gemini. Therefore, when Earth crosses this orbit, the radiant point of falling debris appears in Gemini. Featured here is a composite of many images taken over the past few days through dark skies from Slovakia and capturing the snow-covered peaks of the Belianske Tatra mountains Numerous bright meteor streaks from the Geminids meteor shower are visible. Orion is visible above the horizon, while the bright star nearest the radiant is Castor. APOD Review: RJN's Night Sky Network Lecture
Copyright: Tomáš Slovinský
Προηγούμενες Αστρονομικές Εικόνες της Ημέρας από τη NASA
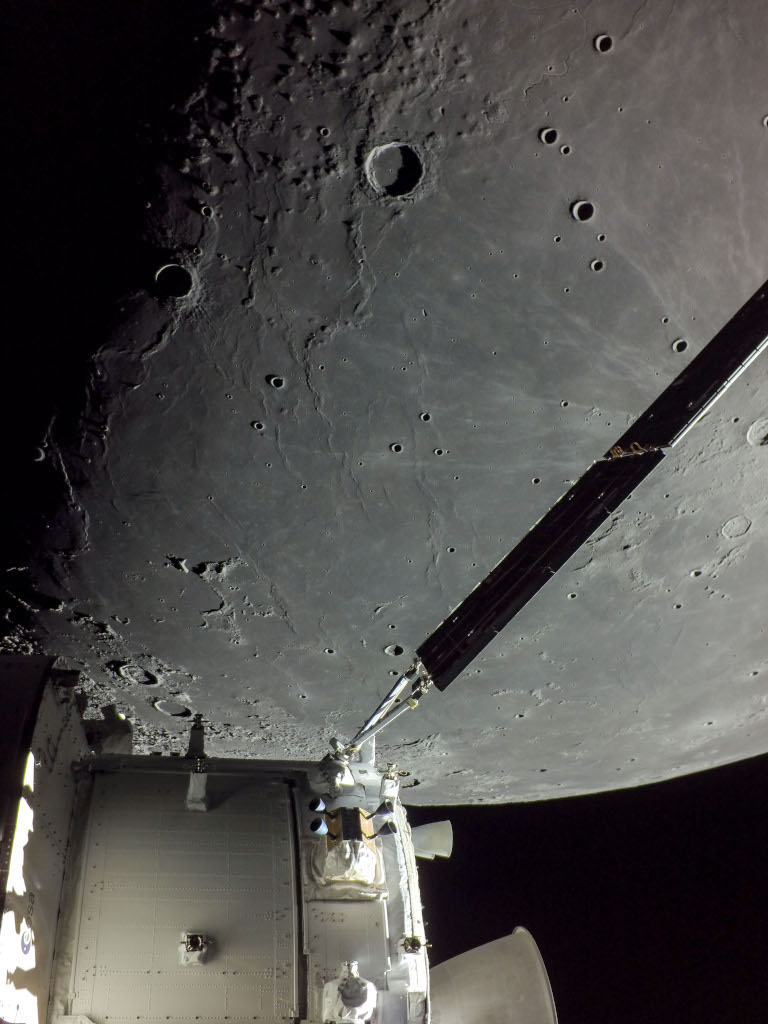
Orion and the Ocean of Storms
13/12/2025
On December 5, 2022, a camera on board the uncrewed Orion spacecraft captured this view as Orion approached its return powered flyby of the Moon. Beyond one of Orion's extended solar arrays lies dark, smooth, terrain along the western edge of the Oceanus Procellarum. Prominent on the lunar nearside Oceanus Procellarum, the Ocean of Storms, is the largest of the Moon's lava-flooded maria. The lunar terminator, the shadow line between lunar night and day, runs along the left of this frame. The 41 kilometer diameter crater Marius is top center, with ray crater Kepler peeking in at the edge, just right of the solar array wing. Kepler's bright rays extend to the north and west, reaching the dark-floored Marius. By December 11, 2022 the Orion spacecraft had returned to its home world. The historic Artemis 1 mission ended with Orion's successful splashdown in planet Earth's water-flooded Pacific Ocean. Watch: The Geminid Meteor Shower
Copyright: NASA
Northern Fox Fires
12/12/2025
In a Finnish myth, when an arctic fox runs so fast that its bushy tail brushes the mountains, flaming sparks are cast into the heavens creating the northern lights. In fact the Finnish word "revontulet", a name for the aurora borealis or northern lights, can be translated as fire fox. So that evocative myth took on a special significance for the photographer of this northern night skyscape from Finnish Lapland near Kilpisjarvi Lake. The snowy scene is illuminated by moonlight. Saana, an iconic fell or mountain of Lapland, rises at the right in the background. But as the beautiful nothern lights danced overhead, the wild fire fox in the foreground enthusiastically ran around the photographer and his equipment, making it difficult to capture in this lucky single shot.
Copyright: Dennis Lehtonen
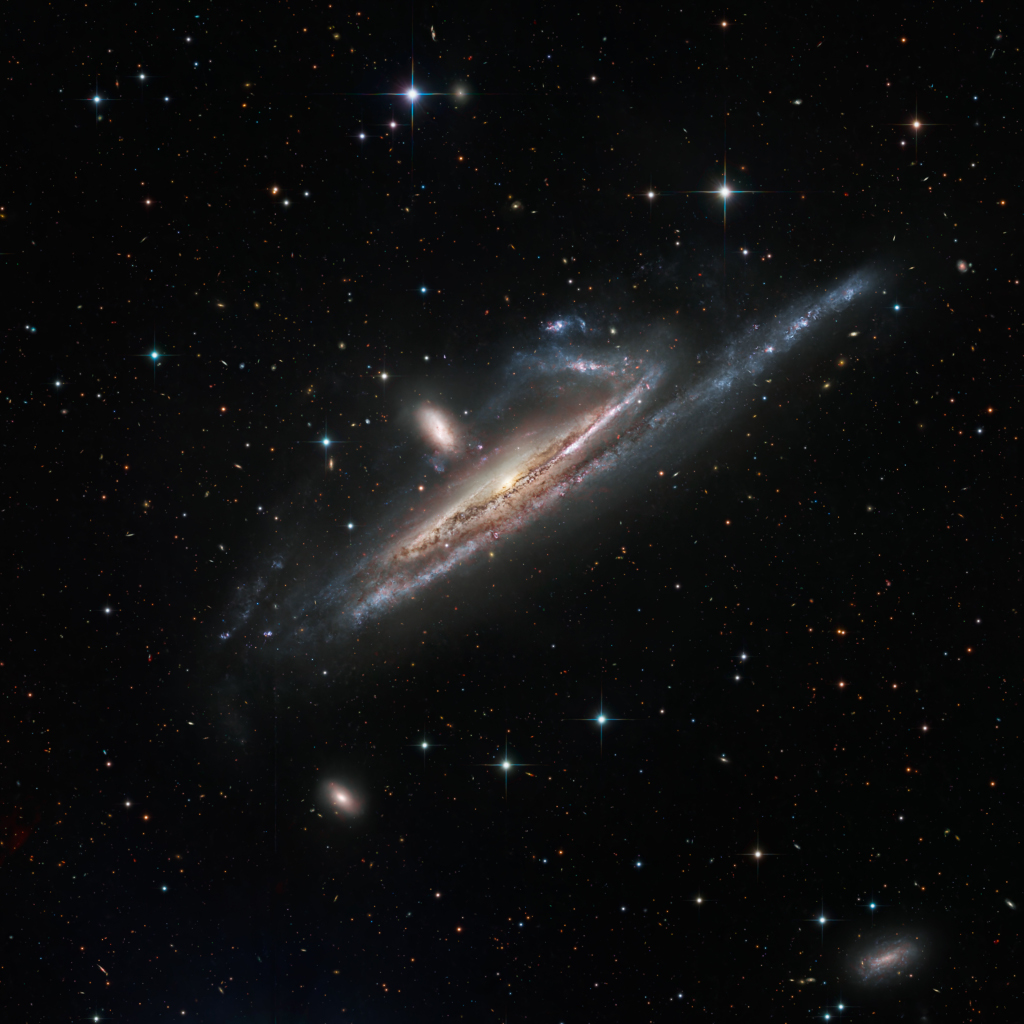
Galaxies in the River
11/12/2025
Large galaxies grow by eating small ones. Even our own galaxy engages in a sort of galactic cannibalism, absorbing small galaxies that are too close and are captured by the Milky Way's gravity. In fact, the practice is common in the universe and illustrated by this striking pair of interacting galaxies from the banks of the southern constellation Eridanus, The River. Located over 50 million light years away, the large, distorted spiral NGC 1532 is seen locked in a gravitational struggle with dwarf galaxy NGC 1531, a struggle the smaller galaxy will eventually lose. Seen nearly edge-on, in this sharp image spiral NGC 1532 spans about 100,000 light-years. The NGC 1532/1531 pair is thought to be similar to the well-studied system of face-on spiral and small companion known as M51.
Copyright: Vikas Chander
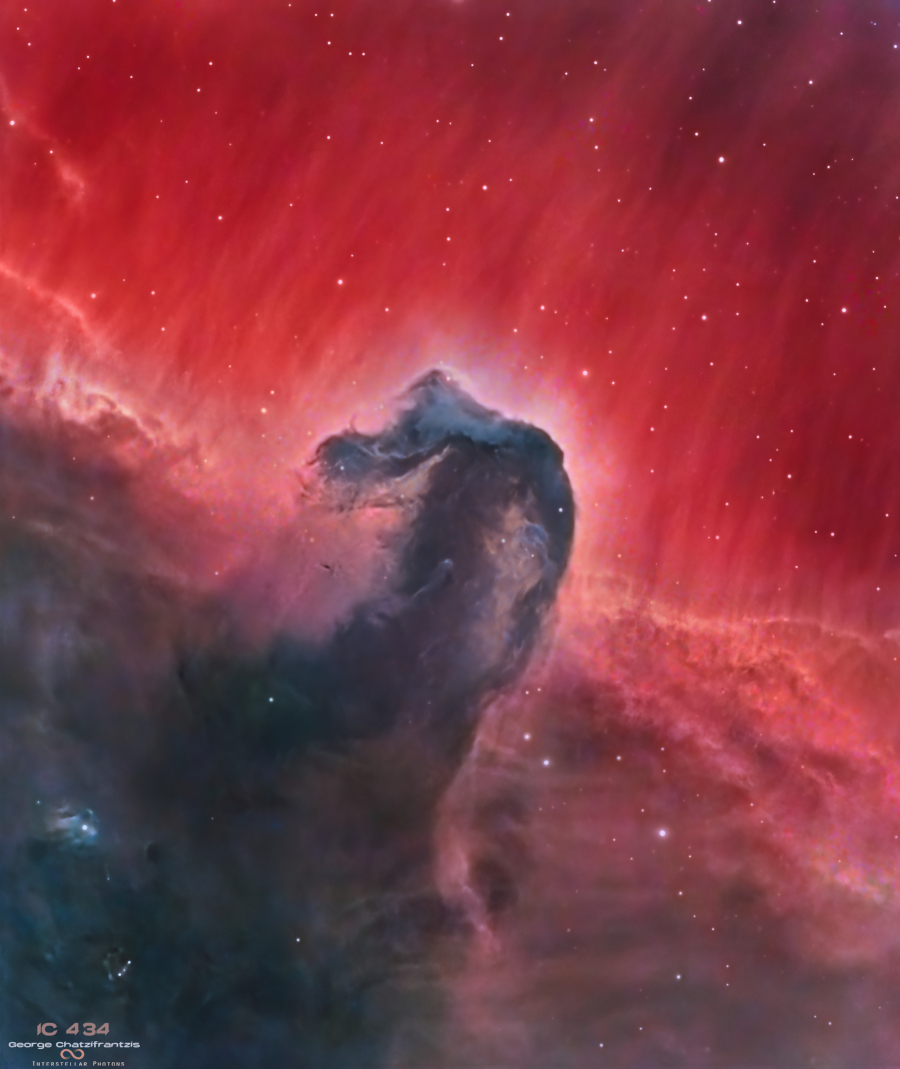
The Horsehead Nebula
10/12/2025
Sculpted by stellar winds and radiation, this dusty interstellar molecular cloud has by chance has assumed an immediately recognizable shape. Fittingly known as The Horsehead Nebula, it lies some 1,500 light-years distant, embedded in the vast Orion cloud complex. About five light-years "tall," the dark cloud is cataloged as Barnard 33, first identified on a photographic plate taken in the late 19th century. B33 is visible primarily because its obscuring dust is silhouetted against the glow of emission nebula IC 434. Hubble space telescope images from the early 21st century find young stars forming within B33. Of course, the magnificent interstellar cloud will slowly shift its apparent shape over the next few million years. But for now the Horsehead Nebula is a rewarding though difficult object to view with small telescopes from planet Earth.
Copyright: George Chatzifrantzis
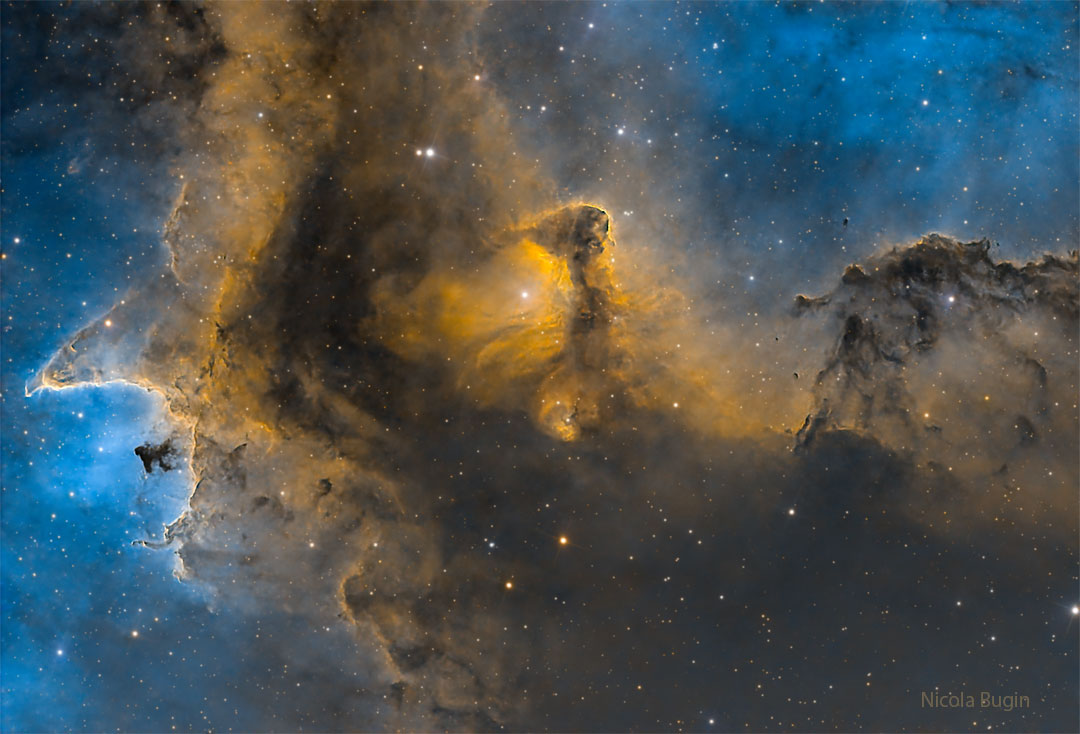
The Heart of the Soul Nebula
09/12/2025
This cosmic close-up looks deep inside the Soul Nebula. The dark and brooding dust clouds outlined by bright ridges of glowing gas are cataloged as IC 1871. About 25 light-years across, the telescopic field of view spans only a small part of the much larger Heart and Soul nebulae. At an estimated distance of 6,500 light-years, the star-forming complex lies within the Perseus spiral arm of the Milky Way, seen in planet Earth's skies toward the constellation of the Queen of Aethiopia (Cassiopeia). An example of triggered star formation, the dense star-forming clouds of IC 1871 are themselves sculpted by the intense winds and radiation of the region's massive young stars. This color image adopts a palette made popular in Hubble images of star-forming regions.
Copyright: Nicola Bugin
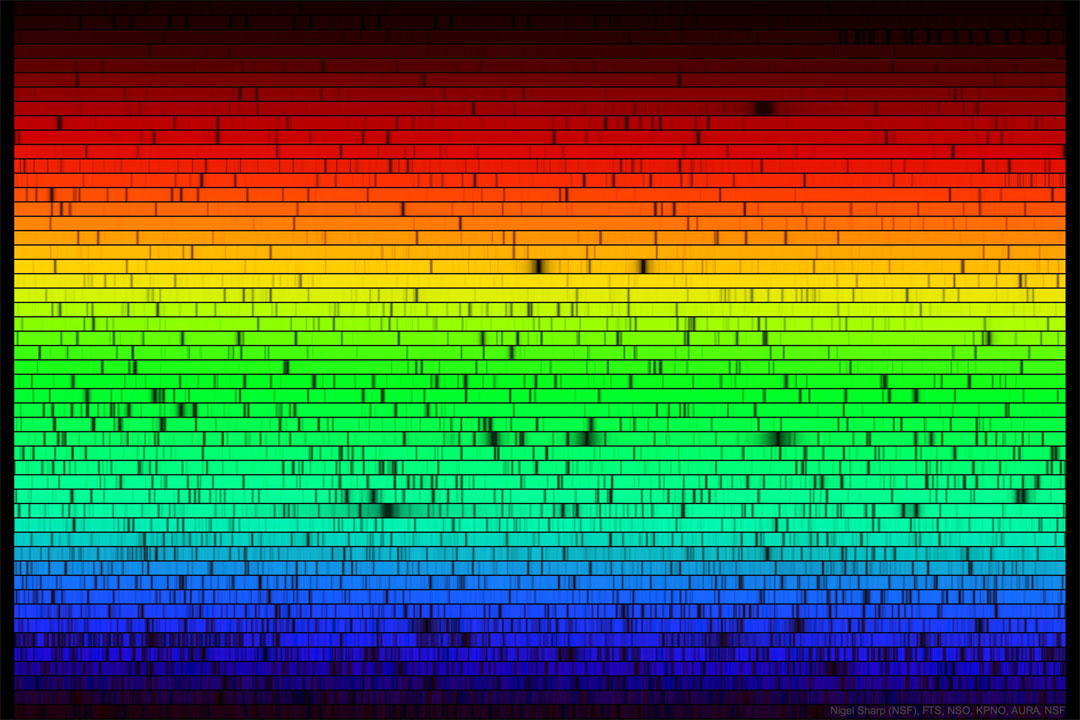
The Sun and Its Missing Colors
07/12/2025
It is still not known why the Sun's light is missing some colors. Here are all the visible colors of the Sun, produced by passing the Sun's light through a prism-like device. The spectrum was created at the McMath-Pierce Solar Observatory and shows, first off, that although our white-appearing Sun emits light of nearly every color, it appears brightest in yellow-green light. The dark patches in the featured spectrum arise from gas at or above the Sun's surface absorbing sunlight emitted below. Since different types of gas absorb different colors of light, it is possible to determine what gasses compose the Sun. Helium, for example, was first discovered in 1868 on a solar spectrum and only later found here on Earth. Today, the majority of spectral absorption lines have been identified - but not all. Free APOD Lecture in Phoenix: Wednesday, December 10 at 7 pm
Copyright: NASA
Apollo 17 at Shorty Crater
06/12/2025
Fifty three years ago, in December of 1972, Apollo 17 astronauts Eugene Cernan and Harrison Schmitt spent about 75 hours on the Moon exploring the Taurus-Littrow valley, while colleague Ronald Evans orbited overhead. This snapshot from another world was taken by Cernan as he and Schmitt roamed the lunar valley's floor. The image shows Schmitt next to the lunar rover parked at the southeast rim of Shorty Crater. That location is near the spot where geologist Schmitt discovered orange lunar soil. The Apollo 17 crew returned with 110 kilograms of rock and soil samples, more than was returned from any of the other lunar landing sites. And for now, Cernan and Schmitt are the last to walk on the Moon.
Copyright: NASA
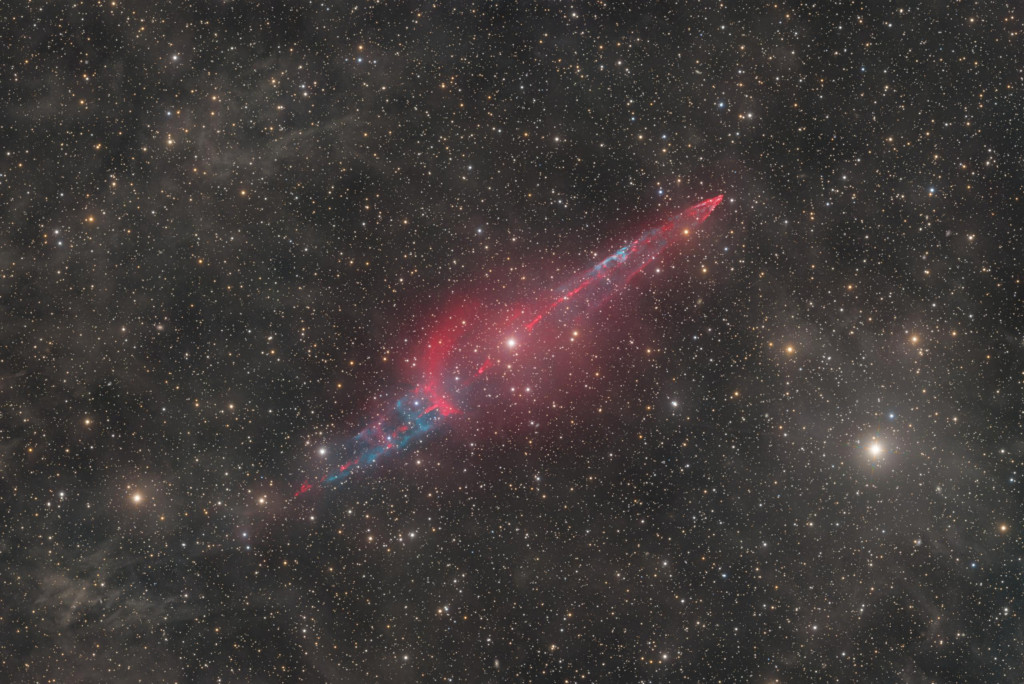
The Bipolar Jets of KX Andromedae
05/12/2025
Blasting outward from variable star KX Andromedae, these stunning bipolar jets are 19 light-years long. Recently discovered, they are revealed in unprecedented detail in this deep telescopic image centered on KX And and composed from over 692 hours of combined image data. In fact, KX And is spectroscopically found to be an interacting binary star system consisting of a bright, hot B-type star with a swollen cool giant star as its co-orbiting, close companion. The stellar material from the cool giant star is likely being transferred to the hot B-type star through an accretion disk, with spectacular symmetric jets driven outward perpendicular to the disk itself. The known distance to KX And of 2,500 light-years, angular size of the jets, and estimated inclination of the accretion disk lead to the size estimate for each jet of an astonishing 19 light-years. Free APOD Lecture in Phoenix: Wednesday, December 10 at 7 pm
Copyright: Tim Schaeffer
Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA (NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day) είναι μια δωρεάν υπηρεσία που παρέχει καθημερινά μια εντυπωσιακή εικόνα από το σύμπαν, την λήψη της οποίας έχει πραγματοποιήσει κάποιος από τους αστρονόμους της NASA ή από κάποιον από τους δορυφόρους ή τα τηλεσκόπια που η NASA λειτουργεί. Οι εικόνες που εμφανίζονται καλύπτουν μια ευρεία γκάμα από θέματα, συμπεριλαμβανομένων των αστερισμών, των γαλαξιών, των πλανητικών συστημάτων, των κομητών, των αστρικών σωμάτων και των παρατηρητηρίων. Κάθε εικόνα συνοδεύεται από μια σύντομη εξήγηση και πληροφορίες σχετικά με το τι παρατηρείται στην εικόνα.